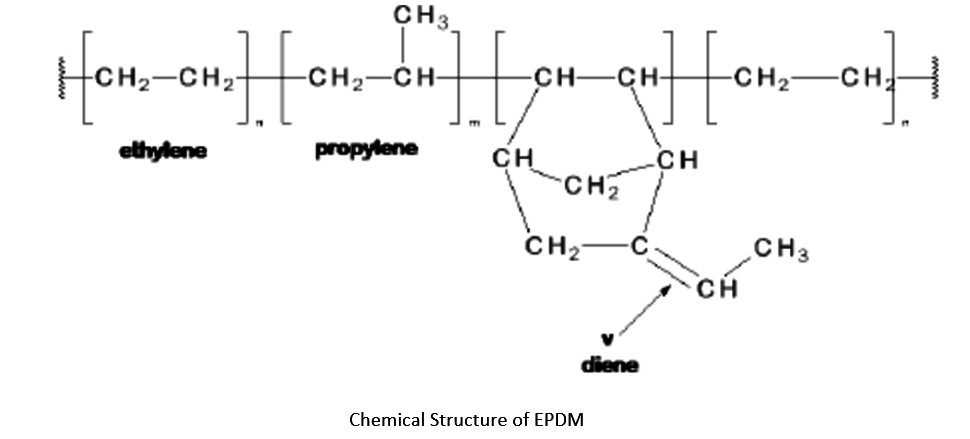
What is EPDM?
EPDM rubber (Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer Rubber) is a type of synthetic rubber used in many applications. The Dienes used in the production of EPDM rubber are ethylidene norbornene (ENB), dicyclopentadiene (DCPD), and vinyl norbornene (VNB). Typically, 4-8% of these monomers are used.
Like most rubbers, EPDM is always mixed with fillers such as carbon black and/or calcium carbonate, and plasticizers such as paraffin oil, and has useful rubber-like properties only when cured. Cross-linking is mainly done by sulphur vulcanization, but also by peroxide (to increase heat resistance) or phenolic resin vulcanization. High-energy radiation such as electron beams are sometimes used to manufacture foams, wires and cables.
1: EPDM and the Construction Industry are the best fit
EPDM rubber products have excellent UV and ozone resistance, long life and elasticity. As a result, EPDM is a highly valuable material in the construction industry (mainly aluminium manufacturing segment, curtain wall industry, UPVC window and door segment – EPDM extruded rubber profiles, EPDM expansion joint profiles segment), accounting for 40% to 45% of EPDM consumption in the world. Within this category, curtain wall systems are the largest application (40%). The road and bridge sector of the construction industry uses his EPDM expansion joints primarily due to their inherent property of ozone resistance. It is also used in basements, landings, ramps and slabs, pools, etc. The use of EPDM in these applications is expected to grow at a higher pace as the construction industry continues to grow.
The global construction industry is expected to reach $8 trillion by 2030, driven primarily by countries such as India, China and the United States.
In the Asia-Pacific region, China has the largest construction market, accounting for 20% of all construction investments worldwide. The country alone is expected to spend about $13 trillion on buildings by 2030.
Construction is India’s second largest industry, contributing around 9% to GDP. The Indian construction industry is projected to become the third largest market in the world by 2035 with a size close to her US$1 trillion.
2: Strong weather resistance
It is quite essential to choose a base elastomer that gives the optimum weather resistance when a product must function in an external area where it is either continuously or occasionally exposed to the elements (such as fenders and benders used at docks). Understanding the various ways that the weather can impact any given elastomer, with the most popular being Sunlight, Temperature, Ozone & UV, Inclement Weather Conditions, is essential when choosing a rubber that can endure the elements for use in any specific application.
Depending on the surrounding temperature, unfavourable weather conditions can take the form of humidity, dew, rain, snow, frost, or hail. When this moisture is paired with solar radiation, it can considerably speed up the weathering of foundation materials. Because of the mechanical strains that are put on a material when moisture is absorbed as well as because moisture plays a chemical role in the chemical development. In addition to the impacts of temperature of a material, structural failures or the acceleration of degradation where it has already begun can be brought on by the freeze/thaw cycle brought on by bad weather.
When creating mixes unique to a particular application, EPDM is compatible with a wide range of other materials and demonstrates exceptional weather resistance, making it a wise choice for usage when products or components are exposed to the elements. Along with a variety of chemicals, diluted acids and alkalis, and heat and weather, EPDM has the capacity to withstand the degrading effects of ozone, oxygen, heat, and weather.
3: EPDM doesn’t require high maintenance
When long-term weather resistance is needed, such as for waterproofing flat roofs of office buildings and homes, it is typically utilised in waterproofing. EPDM applications require little to no maintenance compared to the other elastomers in the market. It is so tough and resilient that it can withstand numerous temperature fluctuations, tears, and abrasions.
4: Strong chemical resistance
EPDM is a flexible elastomer with the favourable qualities, including its resistance to heat and some chemicals that can be moulded into sealing components for many various applications and industries. Grease, sodium hydroxide solutions, and numerous other diluted acids are just a few of the chemical media that EPDM elastomers can resist without suffering any negative effects. It is crucial to remember that EPDM seals do not work well with chemical media that contain fuels, lubricants, and items made of mineral oil. If in doubt, it is always best to consult a sealing expert to ensure that your application is not jeopardised by a subpar sealing solution. EPDM is a suitable elastomer for the majority of common sealing applications.
EPDM seals, especially O-rings and gaskets, are widely used in all kinds of applications and industries. These range from medical devices to water systems to automotive applications. We can also expect to see this EPDM rubber gaskets in various domestic applications such as door/window seals and refrigerators due to their strong combination of thermal and mechanical properties and relative cost effectiveness.
5: High durability
Studies have shown that the thickest and most durable EPDM membranes can last over 40 years. The membrane rarely rips or tears, is durable, yet easy to repair and maintain. The long life and low maintenance increases the value of the investment in such membranes. Even under the harshest conditions, EPDM shows its lifespan as a decisive advantage. The diene monomers, while only form a small part of the composition of EPDM, provide the cross-linking that gives incredible resilience, flexibility and durability. The excellent material properties of EPDM come from this molecular mesh structure and make it unbeatable in terms of elasticity and resistance to ageing.
Due to EPDM’s high durability, it has a wide range of applications, including in vehicles (where it is used for window and door seals, as well as cooling system hoses), expansion joint rubber profiles for bridge construction, EPDM extruded rubber profiles for facades, EPDM seals for cold-rooms, pipe seals, fenders and benders for decks and many others.
Relevant Links: