Sponge Rubber vs. Solid Rubber for Construction: Which is Right for Your Project?
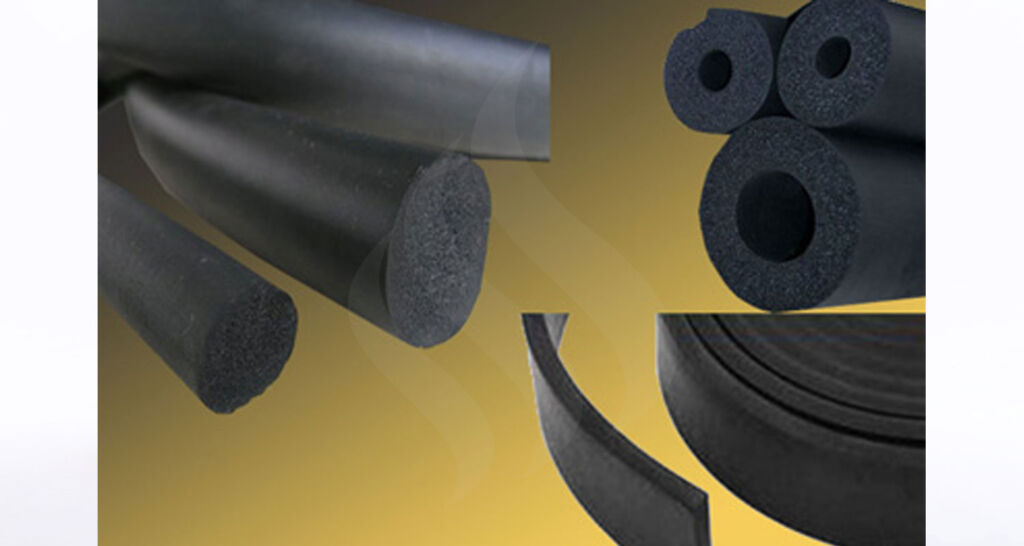



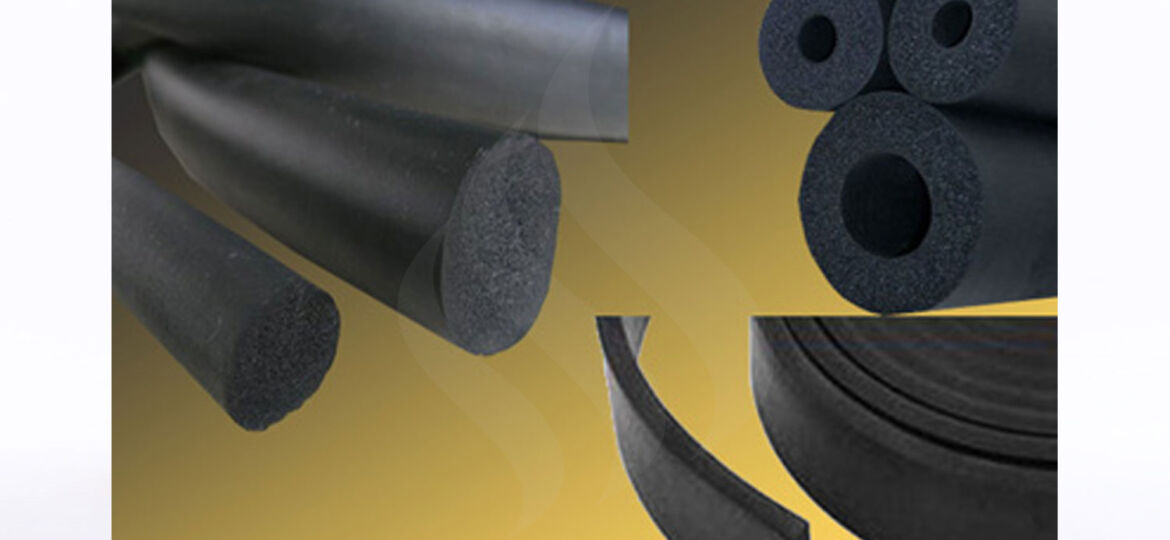
When it comes to choosing the right type of rubber for a specific application, people in manufacturing industry have a variety of options available to them. Two of the most commonly used types of rubber are sponge rubber and solid rubber. While both have their benefits and drawbacks, it’s important to understand the key differences between the two and choose the right type for your specific needs.
- Density: The most obvious difference between sponge and solid rubber is their density. Solid rubber has a higher density than sponge rubber. This means that sponge rubber is lighter than solid rubber, making it ideal for applications where weight is a concern.
- Porosity: Sponge rubber is porous, while solid rubber is not. This porosity makes sponge rubber more compressible and flexible than solid rubber. The sponge rubber can absorb and disperse energy through the open cells, which makes it ideal for shock-absorbing applications.
- Compression Set: Solid rubber has a high compression set, which means that it doesn’t easily return to its original shape after being compressed. In contrast, sponge rubber has a low compression set, which means it can bounce back quickly after being compressed.
- Strength: Solid rubber is stronger and more durable than sponge rubber, which means it can withstand higher stress and strain without deforming or breaking. Sponge rubber is weaker and less durable, which means it is more prone to tearing or breaking.
In this blog, we’ll take a look at the top 5 do’s and don’ts that civil engineers need to know when using sponge rubber vs solid rubber in their applications.
- Do understand the difference in compression set
One of the key differences between sponge rubber and solid rubber is the compression set. Compression set refers to the amount of permanent deformation that a material experiences after being subjected to a load. Sponge rubber has a higher compression set compared to solid rubber, which means that it can deform more under load and take longer to recover its original shape. This is important to consider when selecting the right type of rubber for your application, as it can affect the long-term performance of your product. - Don’t use sponge rubber for high-stress applications
Because of its higher compression set, sponge rubber is not recommended for high-stress applications where solid rubber would be a better choice. High-stress applications, such as heavy-duty machinery, require a material that can withstand high levels of stress and strain without deforming. Solid rubber is better equipped to handle these types of applications as it has a lower compression set and is more resistant to deformation. - Do consider the thermal properties of the rubber
Both sponge rubber and solid rubber have different thermal properties, and it’s important to choose the right type based on your application’s specific needs. Sponge rubber has a lower thermal conductivity compared to solid rubber, which makes it a good choice for applications where insulation is important. On the other hand, solid rubber has a higher thermal conductivity, which makes it a better choice for applications where heat dissipation is important. - Don’t ignore the mechanical properties of the rubber
In addition to considering the thermal properties, it’s also important to take into account the mechanical properties of the rubber. Both sponge rubber and solid rubber have different mechanical properties, such as tensile strength, elongation, and hardness. It is advised to choose the right type of rubber based on the specific mechanical properties required for your application. - Do consider the safety
Safety is a critical factor to consider when choosing between sponge and solid rubber. Both materials can be used in applications where safety is a concern. However, solid rubber is more commonly used in high-impact applications such as flooring and bumpers.




| Application | Sponge Rubber | Solid Rubber |
| Construction Industry | Expansion joints for building structures, insulation materials, sealing products | Expansion joints for roads and bridges, roofing, waterproofing, electrical insulation, weather-stripping |
| Automotive Industry | Engine mounts, seals, gaskets, suspension components | Tires, engine components, hoses, belts |
| Cushioning and Shock Absorption | Athletic shoes, sport padding, furniture padding, package cushioning | Car tires, industrial flooring, conveyor belts, heavy-duty bumpers and fenders |
| Sealing and Insulation | Gaskets, O-rings, weather-stripping, HVAC insulation | Seals, gaskets, hoses, diaphragms, vibration dampers |
| Acoustics | Sound-absorbing materials, noise reduction, soundproofing | Speaker components, acoustic paneling, vibration isolation |
| Medical Devices | Prosthetics, orthotics, soft support products, medical foam cushions | Durable medical equipment, hard orthotic supports, medical tubing |
SagaFlex offers sponge products in various elastomeric materials like EPDM, Neoprene, Nitrile, Silicone, etc that are ideal for cushioning and shock absorption applications, as well as for sound insulation and acoustics. SagaFlex products are used in a variety of industries, including automotive, construction, and medical, among others.
SagaSeal offers seals solid as well as sponge using various elastomeric materials like EPDM, Neoprene, Nitrile, Silicone, etc which are manufactured using high-quality raw material and superior process. The SagaSeal products are commonly used to create an air, dust and watertight seals. SagaSeals of EPDM are great for use in outdoor sealing applications due to the superior UV and Ozone resistance that the material offers.
To conclude, sponge rubber and solid rubber both have their unique benefits and drawbacks, and the right choice depends on the specific needs of your application. When choosing between the two, it’s important to consider factors such as compression set, thermal properties, mechanical properties, and cost. By taking the time to carefully evaluate these factors, architect, planners and civil engineers can choose the right type of rubber to ensure their products perform to the best of their ability.